Gynecomastia Solutions: Must-Have Tips for Best Results
Gynecomastia: Understanding, Causes, and Treatment Options
Gynecomastia is a common condition and has now become the most common aesthetic procedure in males, characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. While it can affect one or both breasts and may sometimes be uneven, gynecomastia often causes physical discomfort and emotional distress. Understanding what causes this condition, how it is diagnosed, and what treatment options are available can help those affected safely manage or overcome it.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of the glandular tissue of the male breast. Unlike fat accumulation alone (which is called pseudogynecomastia or lipomastia), gynecomastia involves a proliferation of the actual breast tissue due to hormonal imbalances or other underlying issues. It is a fairly common condition, affecting males across various age groups—from newborns and adolescents to the elderly.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Hormonal imbalances are the primary drivers of gynecomastia. Specifically, it results when there is an increase in estrogen activity relative to androgen activity in the body. Several factors can lead to this hormonal change:
- Puberty: During adolescence, hormone levels fluctuate dramatically, often causing transient gynecomastia. This usually resolves within a few months to a couple of years. About 30% of males experience gynecomastia as they travel through puberty but most of these resolve in a couple of years.
- Aging: As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline while relative estrogen levels might increase, leading to breast tissue growth.
- Medications: Several drugs can cause gynecomastia as a side effect, including certain anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, some antipsychotics, and heart medications such as spironolactone.
- Health conditions: Liver disease, kidney failure, hyperthyroidism, and tumors of the testes or adrenal glands can disrupt hormonal balance, triggering gynecomastia.
- Lifestyle factors: Excessive alcohol consumption, use of recreational drugs like marijuana or heroin, and obesity can contribute to the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The most noticeable symptom is the enlargement of the male breast tissue, which can sometimes be tender to the touch. Men may also notice nipple sensitivity or mild pain. In some cases, the enlarged tissue appears as a firm, rubbery disk under the nipple.
Diagnosing gynecomastia involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and sometimes further testing. Physicians typically differentiate gynecomastia from other causes of breast enlargement such as lipomastia or breast cancer, which, though rare in men, needs to be ruled out. Blood tests to check hormone levels, liver and kidney function, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or mammography may also be part of the evaluation.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the breast enlargement. In many cases, especially with pubertal gynecomastia, the condition resolves spontaneously without treatment.
- Medical therapy: If gynecomastia is caused by medications or other reversible factors, stopping or changing the offending agent is recommended. Hormonal therapies such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors are sometimes used but typically reserved for persistent or severe cases.
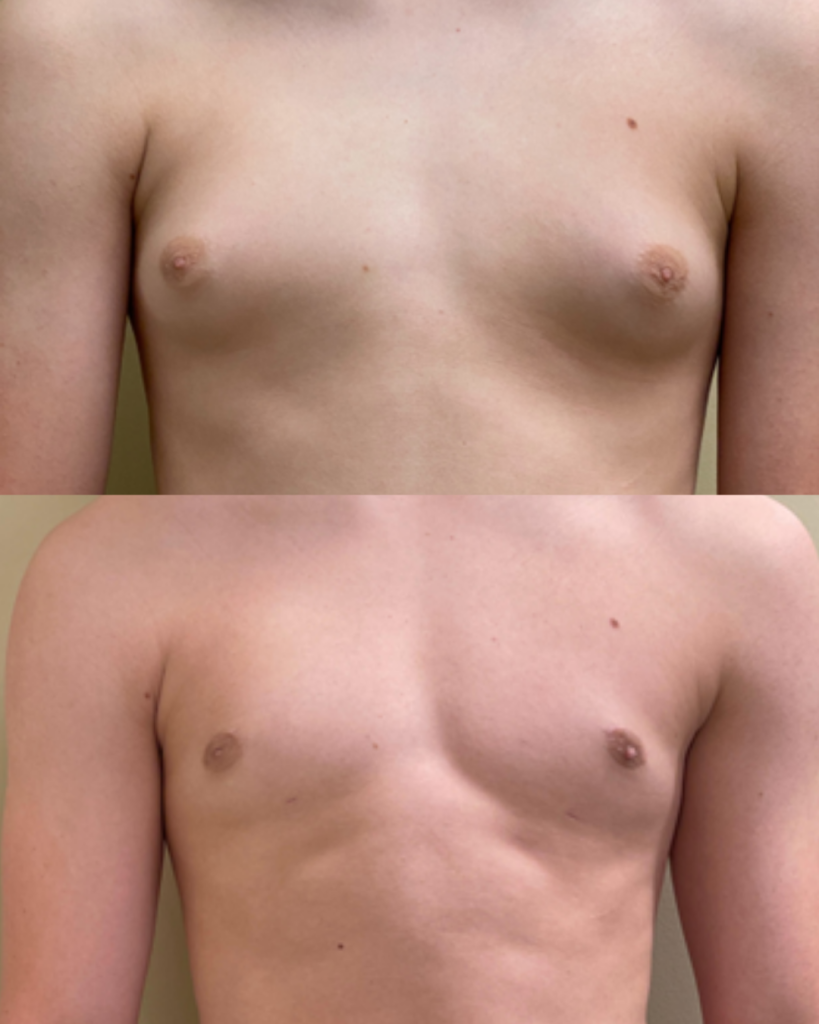
- Surgical intervention: For patients with significant, persistent gynecomastia or those bothered by the cosmetic and psychological effects, surgery may be an option. Liposuction combined with excision of glandular tissue can restore a flatter, more typical male chest contour. Most gynecomastia patients can have the procedure performed in the office with oral sedation and local anesthesia.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Weight loss and exercise can reduce fat deposits in the chest area and sometimes improve the appearance, though fat loss alone doesn’t eliminate glandular tissue.
Psychological Impact and Support
Gynecomastia can cause embarrassment, anxiety, and lowered self-esteem. Many men may avoid activities such as swimming or changing in public, leading to social withdrawal. It is important to address these emotional components and seek support from healthcare professionals or counseling services when needed.
When to See a Doctor
If breast enlargement appears suddenly, is accompanied by pain or nipple discharge, or if there is a noticeable lump that feels particularly hard or fixed, medical evaluation is necessary. Early diagnosis can help identify any underlying conditions and initiate appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a widespread but frequently misunderstood condition. Being knowledgeable about its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers men to seek help and find effective management strategies. Whether through watchful waiting, medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery, many men find relief and regain confidence following their diagnosis. If you suspect you have this condition, consult a healthcare provider to explore the best options tailored to your needs.
Gynecomastia Removal is the Most Common Aesthetic Procedure Performed in Men. Usually an Office Procedure with Oral Sedation and Local Anesthesia